구현 문제입니다.
문제 조건 자체는 이해하기 어려운 부분은 딱히 없는거 같습니다.
하지만, 이것을 코드로 구현하려니 마땅한 아이디어가 떠오르지 않았습니다.
3~4일간 이 문제만 붙잡고 백준 질문게시판에서 얻은 테스트 케이스를 직접 써보면서 경우의 수를 확인하고,
수많은 디버깅을 한 끝에 맞출 수 있었습니다.

제가 문제를 해결한 방법을 아래 글을 통해 공유하겠습니다.
1. 그래프로 윷놀이 판 구현하기
문제에서 주어지는 주사위 윷놀이 판의 모습은 아래 그림과 같습니다.
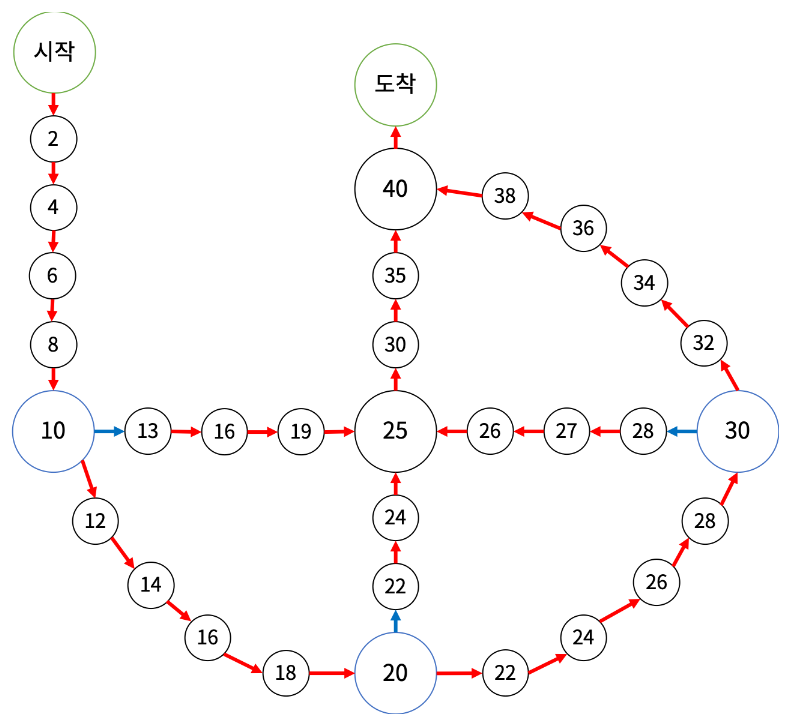
이 모습을 보자마자 그래프를 떠올렸고, 그림을 그래프로 표현하고자 했습니다.
우선 파란색으로 갈 수 있는 곳을 지름길(Shortcut)이라 가정했습니다.
💡 [10, 20, 30에서 출발해 40까지의 길이 모두 지름길입니다.]
💡 [편의상 빨간색으로만 갈 수 있는 길을 둘레길이라 하겠습니다.]
또, 특정 숫자는 두 가지 길이 있습니다.
예를 들어, 22번은 20에서 시작할 경우 지름길로 가 24 수도 있지만,
지름길이 아닌 빨간색 경로를 따라 또 다른 24로 갈 수 있습니다.
다행히 이렇게 겹치는 번호는 지름길이 유무이거나 앞 뒤로 연결된 번호가 다르다는 것입니다.
따라서 지름길 또는 앞, 뒤로 연결된 정보로 움직임을 확정지을 수 있습니다.
private static class Node {
int before; // 뒷 번호
int from; // 현재 번호
int to; // 앞 번호
boolean isShortCut; // 지름길
Node(int before, int from, int to, boolean isShortcut) {
this.before = before;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.isShortCut = isShortcut;
}
...
}private static final List<List<Node>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
// 게임 판 생성
private static void makeGraph() {
// 코드가 너무 길어 본 코드에서 확인하세요
}
저의 경우 빨간색 둘레길을 먼저 생성하여 그래프의 첫 번째에 두고,
파란색 지름길을 그래프의 두 번째에 두었습니다.
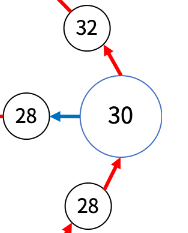
여기서 예상치 못한 문제를 발견했습니다.
바로 30번입니다.
아래 그림과 같이 30번만 세 가지 길이 존재합니다.
 |
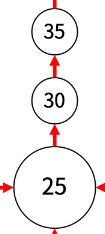 |
위 그림에 의해 제가 만든 그래프는 30번의 경우 아래와 같이 저장됩니다.
graph.get(30).get(0) // 28 -> 30 -> 32
graph.get(30).get(1) // 28 -> 30 -> 28
graph.get(30).get(2) // 25 -> 30 -> 35
30번의 0과 1번째는 이전의 값이 28로 똑같기 때문에 ,파란색 지름길인지 혹은 다음 번호로 확인해야 합니다.
30번의 2번째는 파란색 지름길이기 때문에, 이전 번호 혹은 다음 번호로 확인해야 합니다.
💡 [위에서 10, 20, 30에서 시작해 40까지 갈 수 있는 모든 경로를 파란색 지름길로 상정한다 했습니다.]
2. 말판 움직이기
말판은 총 네개가 존재합니다.
또, 입력으로 주사위가 나올 수 10개가 주어집니다.
네 개의 말판을 길이가 10인 중복 순열로 만들고,
각 말판이 만들어진 순열에 따라 움직이면 됩니다.
주의점은 크게 두 가지가 있습니다.
- 만들어진 순열에 따라 움직이기 때문에, 이미 도착 지점에 도착한 말판은 움직일 수 없다.
- 문제 조건에 의해 이동을 완료한 지점에 다른 말판이 존재하면 안된다.
이 두 가지 주의점을 만족하지 못하면 불가능한 방법이므로,
과감하게 해당 중복 순열로 만들어진 방법은 무시하시면 됩니다.
3. 문제 접근 순서
- graph로 윷놀이 판 생성
- 말판의 중복 순열 생성
- 중복 순열에 따른 말판 이동
[구현 코드]
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
private static final int N = 10;
private static final int M = 4;
private static final int START = 0;
private static final int END = 42;
private static final int[] moves = new int[N];
private static final List<List<Node>> graph = new ArrayList<>();
private static int max = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer stz = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
moves[i] = Integer.parseInt(stz.nextToken());
}
makeGraph();
int[] order = new int[N];
makeOrder(order, 0); // 중복 순열
System.out.println(max);
br.close();
}
// 게임 판 생성
private static void makeGraph() {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>()); // 0
graph.add(new ArrayList<>()); // 1
// 빨간색길 먼저 생성
graph.get(START).add(new Node(START, START, START + 2, false));
for (int i = START + 2; i <= END; i++) {
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
if (i % 2 == 0) {
graph.get(i).add(new Node(i - 2, i, i + 2, false));
}
}
// 지름길 생성
// 10 ~ 25
graph.get(10).add(new Node(8, 10, 13, true));
for (int i = 13; i <= 16; i += 3) {
graph.get(i).add(new Node(i - 3, i, i + 3, true));
}
graph.get(19).add(new Node(16, 19, 25, true));
// 20 ~ 25
for (int i = 20; i <= 22; i += 2) {
graph.get(i).add(new Node(i - 2, i, i + 2, true));
}
graph.get(24).add(new Node(22, 24, 25, true));
// 30 ~ 25
graph.get(30).add(new Node(28, 30, 28, true));
for (int i = 27; i >= 26; i--) {
graph.get(i).add(new Node(i + 1, i, i - 1, true));
}
graph.get(28).add(new Node(30, 28, 27, true));
// 25 ~ 40
// 25로 가는 경우는 19, 24, 26이 있지만 결국 25에서 한 쪽 방으로만 움직이므로 -1로 함
graph.get(25).add(new Node(-1, 25, 30, true));
for (int i = 30; i <= 35; i += 5) {
graph.get(i).add(new Node(i - 5, i, i + 5, true));
}
}
// 중복 순열 생성
private static void makeOrder(int[] order, int depth) {
if (depth == N) {
max = Math.max(max, moving(order));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
order[depth] = i;
makeOrder(order, depth + 1);
}
}
// 만들어진 순열에 맞춰 윷놀이 이동
private static int moving(int[] order) {
int total = 0;
Node[] locations = new Node[M];
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
locations[i] = new Node(START, START, START + 2, false);
}
Loop1: for (int t = 0; t < N; t++) {
int mal = order[t];
int power = moves[t];
Node currentNode = locations[mal];
// 도착지점에 있는 것을 움직이려고 할 경우 -> 불가능함(만들어진 순열에 따라서만 움직여야 됨)
if(currentNode.from == END){
total = 0;
break;
}
// 주사위 결과에 따른 이동지점
Node nextNode = nextLocation(currentNode, power);
// 이미 다른 말판이 이동하고자 하는 자리에 있을 경우
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
// 문제 조건에 의해 이동지점이 도착인 경우 가능
if(locations[i].from == END) continue;
// 이동을 마치는 칸에 다른 말이 있으면
if ((locations[i].isEqualNode(nextNode))) {
total = 0;
break Loop1;
}
}
locations[mal] = nextNode;
total += nextNode.from;
if(nextNode.from == END) total -= END;
}
return total;
}
private static Node nextLocation(Node currenNode, int power) {
Node cn = currenNode;
while (power-- > 0) {
if (cn.from == END) break;
if (graph.get(cn.to).size() == 2) {
cn = (!cn.isShortCut) ? graph.get(cn.to).get(0) : graph.get(cn.to).get(1);
} else if (graph.get(cn.to).size() == 1) {
cn = graph.get(cn.to).get(0);
} else {
// 30일 때
if (!cn.isShortCut) {
cn = graph.get(cn.to).get(0);
} else {
if (cn.before == -1) {
cn = graph.get(cn.to).get(2); // 25 -> 30 일 경우
} else {
cn = graph.get(cn.to).get(1); // 28 -> 30 일 경우
}
}
}
}
if (cn.from == 10) {
cn = graph.get(10).get(1);
} else if (cn.from == 20) {
cn = graph.get(20).get(1);
} else if (cn.from == 30) {
if(cn.to != 35) {
cn = graph.get(30).get(1);
}
}
return cn;
}
private static class Node {
int before; // 뒷 번호
int from; // 현재 번호
int to; // 앞 번호
boolean isShortCut; // 지름길
Node(int before, int from, int to, boolean isShortcut) {
this.before = before;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
this.isShortCut = isShortcut;
}
public boolean isEqualNode(Node node) {
if(this.before != node.before || this.from != node.from ||
this.to != node.to || this.isShortCut != node.isShortCut) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
}
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 - 3197 백조의 호수(Java) (0) | 2023.09.30 |
|---|---|
| 프로그래머스 - 상담원 인원 (Java) (4) | 2023.08.08 |
| 백준 - 17822 원판 돌리기 (0) | 2023.07.22 |
| SW Expert - 달란트 2 (Java) (0) | 2023.07.19 |
| SW Expert - 1812 수정이의 타일 자르기(Java) (0) | 2023.07.17 |



